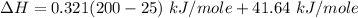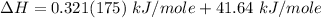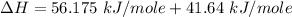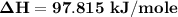Answer:
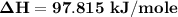
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
The molecular formula =
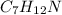
The normal boiling point = 200°C
The enthalpy of the vapor = 200°C
The liquid temperature = 25°C.
By applying Kopp's rule:
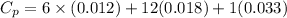
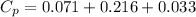
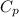 = 0.32 kJ/mole
= 0.32 kJ/mole
For Trouton's rule;
ΔHV = 0.088 Tb(t) for non polar liquid
ΔHV = 0.088(200)°C
ΔHV = 0.088(200+ 273.15)
ΔHV = 41.637 kJ/mol
ΔHV ≅ 41.637 kJ/mol
∴
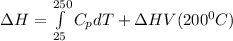
Replacing the values from above; we have: