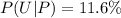Answer:
The probability is
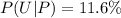
Explanation:
Generally a true positive means that the person tested is a drug user and he/she test positive to the test
while true negative mean that the person tested is not a drug user and he/she test negative to the test
From the question we are told that
The probability that a person test positive to the drug test given that the person is a drug user is
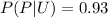
Here P => event that a person test positive to the drug test
U => event that the person is a drug user
The probability that a person test negative to the drug test given that the person is not a drug user is
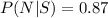
Here N => event that a person test negative to the drug test
S => event that the person is not a drug user
The probability that a person is a drug user is
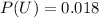
Generally the probability that a person test positive to the test given that the person is a non- user is
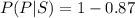
=>
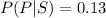
Generally the probability that a person is a non user of drug is
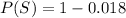
=>
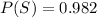
Generally the probability that a person test positive to the drug test is mathematically evaluated as
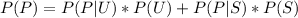
=>
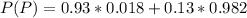
=>
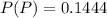
Generally the probability a person is a user given that he or she tested positive is mathematically represented as
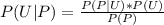
=>
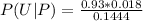
=>
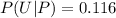
Converting to percentage
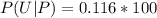
=>