Answer: 0.0475
Explanation:
Let x = random variable that represents the number of a particular type of bacteria in samples of 1 milliliter (ml) of drinking water, such that X is normally distributed.
Given:
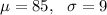
The probability that a given 1-ml will contain more than 100 bacteria will be:
![P(X>100)=P((X-\mu)/(\sigma)>(100-85)/(9))\\\\=P(Z>1.67)\ \ \ \ [Z=(X-\mu)/(\sigma)]\\\\=1-P(Z<1.67)\ \ \ [P(Z>z)=1-P(Z<z)]\\\\=1- 0.9525=0.0475](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ed4fws4tqsti6rwqbjrr92n7k6grfeckqr.png)
∴The probability that a given 1-ml will contain more than 100 bacteria
0.0475.