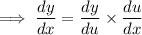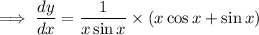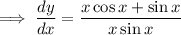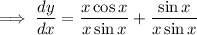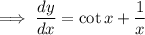Answer:
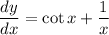
Explanation:
![\boxed{\begin{minipage}{6 cm}\underline{Product\:Rule}\\\\$(d)/(dx)[f(x)g(x)]=f(x)g'(x)+f'(x)g(x)$\\\\\\\underline{Chain\:Rule}\\\\$(dy)/(dx)=(dy)/(du) * (du)/(dx)$\\\end{minipage}}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/9p65lqs1a2lisdqxxxk0.png)
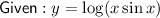
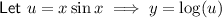
Using the product rule, differentiate y with respect to
 :
:
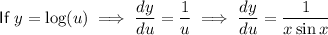
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Differentiate
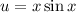 with respect to x using the product rule:
with respect to x using the product rule:
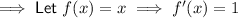
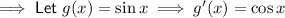
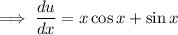
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Use the chain rule to differentiate y with respect to x: