Answer:
Answer with explanation is below~
Explanation:
We could easily obtain the formulae/formula of an equilateral triangle not only through Pythagoras Theorem, but also through Heron's formula.
INTRODUCTION:
What's equilateral triangle?
- It's an triangle, whose all sides're of equal measurement.
What's Heron Formula?
- It's just a formula actually,take an example:Let,a,b and c denotes the lengths of 3 sides of any triangle,then the area will be given as:
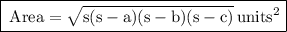
Where,
- s = (a+b+c)/2 {Half of the perimeter, basically}
What's Pythagoras' Theorem?
- It's actually like a formula but a theorem introduced by Pythagoras.
SOLVING:
Let,ABC an equilateral triangle of sides a.
Now:Draw a perpendicular straight line AM to the side BC(Name each part of triangle)
So it's clear that ∆AMB is a right angled triangle at M, BM = (1/2)BC = a/2.
Please note AM here represents the height of ∆ ABC.
- Let's use Pythagoras' theorem now.
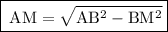
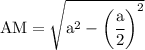
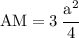
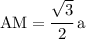
Now find the area of ∆ABC:
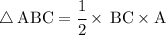
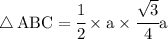
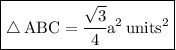
Hence,the formulae of equilateral triangle using Pythagoras' theorem is {√(3)/4} a^2

Extras:
Now let's find the area using Heron's Formula.
Solving:
Let each side of an equilateral triangle be a.
SO, then:
s = (3a/2)
We know that, (Heron's formula)
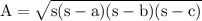
Now the area A :
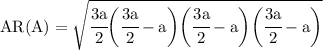
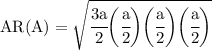
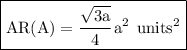
And voila! we're done!
I hope this helps! :)
[Figure of Equilateral triangle is attached, it denotes the triangle we need to draw while finding the formulae through Pythagoras' theorem. ]