Answer:
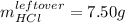
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, since the undergoing chemical reaction is:

In order to identify the limiting reactant, we compute the available moles of sodium hydroxide (molar mass = 40 g/mol) and the moles of hydrochloric acid consumed by those moles via their 1:1 mole ratio considering the chemical reaction:
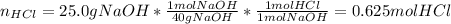
Next, since the molar mass of hydrochloric acid is 36.46 g/mol, we compute the mass of that reactant that is actually consumed:
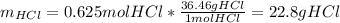
In such a way, the leftover of HCl is:
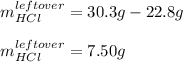
Best regards!