Answer:
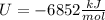
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, since the heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter, we can use this found value on ethernet: 5.86 kJ/°C, thus, we can compute the heat gained by the calorimeter:
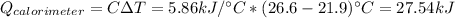
Thus, since the heat gained by the calorimeter is actually the heat released due to the combustion of byphenyl, we compute it as the negative of that of the calorimeter:
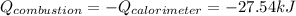
Finally the energy of reaction, U, in kJ/mol for the combustion of byphenyl (molar mass = 154 g/mol) is:
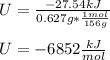
Best regards!