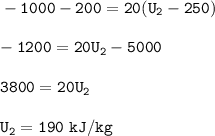The final specific internal energy : 190 kJ/kg
Further explanation
The laws of thermodynamics 1 state that: energy can be changed but cannot be destroyed or created
The equation is:
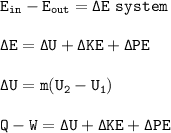
Energy owned by the system is expressed as internal energy (U)
This internal energy can change if it absorbs heat Q (U> 0), or releases heat (U <0). Or the internal energy can change if the system does work or accepts work (W)
The sign rules for heat and work are set as follows:
• The system receives heat, Q +
• The system releases heat, Q -
• The system does work, W -
• the system accepts work, W +
A closed system of mass 20 kg⇒m=20 kg
Heat transfer of 1000 kJ from the system to the surroundings⇒Q=-1000 kJ
The work done on the system is 200 kJ⇒W=+200 kJ
The initial specific internal energy of the system is 250 kJ /kg⇒U₁ = 250 kj/kg
Neglect changes in kinetic and potential energy⇒ΔKE+ΔPE=0, so
Q-W = ΔU
Input in equation