Answer:
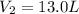
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, we can consider this problem related to ideal gases which are those that are not attracted or repulsed to each other, and can be studied via the ideal gas equation:
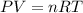
Thus, since we have two conditions and the moles of the gas have not changed, we can write:
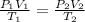
Because the initial conditions for 10.0 L of the gas are 1 atm and 273.15 K (STP) and the final conditions are 800 mmHg (1.053 atm), so the new volume is:
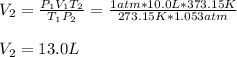
Best regards!