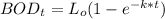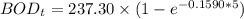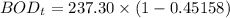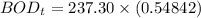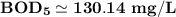Answer:
The value of
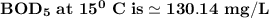
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information:
To find the BOD5 (in mg/L) at 15° C; we need to know the ultimate carbonaceous BOD and the reaction rate coefficient at 15° C.
So, to start with the calculation of the ultimate carbonaceous BOD by using the formula:
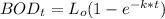
where;
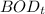 = Biochemical oxygen demand at t days
= Biochemical oxygen demand at t days
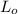 = the ultimate carbonaceous
= the ultimate carbonaceous
∴
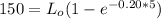
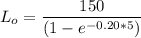
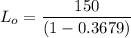
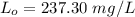
Thus, the ultimate carbonaceous BOD = 237.30 mg/L
For the reaction rate coefficient; we use the formula:
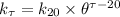
where;
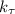 = rate of the reaction constant at various temperature (T) = 15
= rate of the reaction constant at various temperature (T) = 15
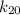 = rate of the reaction constant at standard laboratory = 0.20
= rate of the reaction constant at standard laboratory = 0.20
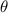 = constant = 1.047
= constant = 1.047
∴
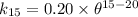
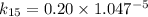
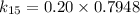
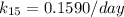
Thus, at 15° C, the reaction constant (k) = 0.1590 / day
Finally, the BOD5 (in mg/L) at 15° C can be calculated by using the formula: