Answer:
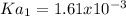
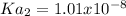
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, since the stepwise dissociation of malonic acid which is a diprotic acid that we are going to symbolize by H₂A, is:
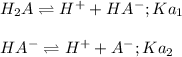
The first ionization has the following equilibrium expression:
![Ka_1=([H^+][HA^-])/([H_2A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/a73hglkhnlesjixfl3haztlgzuj581ynt3.png)
Whereas the concentration of H⁺ equals the concentration of HA⁻ and is computed via the pH:
![[H^+]=[HA^-]=10^(-pH)=10^(-1.47)=0.0339M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/njfxhheu22ar9wtoyntrx2xur2kfzgb2cx.png)
Next, we compute the molarity of the 19.5 g of malonic acid (molar mass = 104.06 g/mol) as shown below:
![[H_2A]=(19.5g/(104.06 g/mol))/(0.250L)=0.750M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/77d7xkrdit9qqggbab9jrkf17dz4puzj60.png)
Thus, Ka1 turns out:
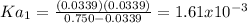
Now, for the second ionization, since the 0.300-M sodium hydrogen malonate is the source of HA⁻, and the pH is 4.26, we can compute the concentration of both H⁺ and A⁻² again by considering the pH:
![[H^+]=[A^-^2]=10^(-4.26)=5.50x10^(-5)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ev9kfns2avzfyjr405rw2lpey8itxkh68r.png)
Therefore Ka2 turns out:
![Ka_2=([H^+][A^(-2)])/([HA^-])=((5.50x10^(-5))(5.50x10^(-5)))/(0.300-(5.50x10^(-5)))\\ \\Ka_2=1.01x10^(-8)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/irj03vj759k7nfwpwyjtvz1c14jfb2ovwo.png)
Best regards!