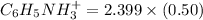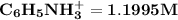Here is the correct format for the question.
An aqueous solution contains dissolved
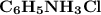 and
and
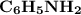 . The concentration of
. The concentration of
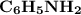 is 0.50 M and pH is 4.20. Calculate the concentration of
is 0.50 M and pH is 4.20. Calculate the concentration of
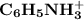 in this buffer solution.
in this buffer solution.
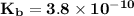
Answer:
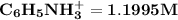
Step-by-step explanation:
From the above information:
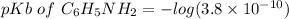
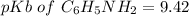
pH = 4.20
pOH = 14 - pH
pOH = 14 - 4.20 = 9.8
According to Henderson Hasselbalch equation
![pOH = pKb + log ([C_6H_5NH_3^+])/([C_6H_5NH_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nkul2khjsykdtwsj1yd4rikcrdxg8ha40t.png)
![9.8 = 9.42 + log ([C_6H_5NH_3^+])/((0.50))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/eo8ccm0qjuzsogxvp5o40qutzk4n1mx5fz.png)
![9.8-9.42 = log ([C_6H_5NH_3^+])/((0.50))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cu6tkibiubftnjhu3fkutipln5jrqp30c3.png)
![0.38 = log ([C_6H_5NH_3^+])/((0.50))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/9tayo167wv5jzaf9p1w0oc45gcy16e25e6.png)
![10^(0.38) = ([C_6H_5NH_3^+])/((0.50))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qlhr9owfjr2qefek2ql0ah9l8v4f94pe1p.png)
![2.399 = ([C_6H_5NH_3^+])/((0.50))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/rtvn4pdg7mlxqsygdkgl98cfzqu0q3zis1.png)