Answer:
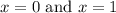
Explanation:
We are given and asked to solve the equation:
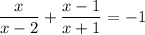
We can first remove the rational expressions by multiplying both sides of the equation by its LCM (in this case, by (x - 2)(x + 1)):
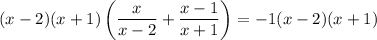
Simplify:

Expand and isolate:
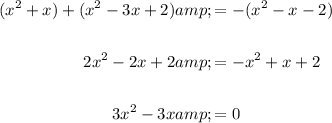
Hence solve for x:
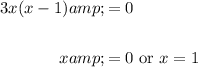
In conclusion, the solutions of the equation are x = 0 and x = 1.