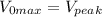Answer:
1) a) i) V =
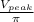
ii) V =
![V_(peak) [ 1 - (1)/(2fR_(l) C) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/4lgnw7n6hsz9yu7e7incsaivaq0r21yyio.png)
b) i) V =
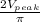
ii) V =
![V_(peak) [ 1 - (1)/(4fR_(L)C ) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/d5i7trngzyxmioqvvvu7ndko6ayuadx6sm.png)
2) a) 2Vpeak
b) P/ V =
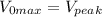
Step-by-step explanation:
1) If the diodes were ideal
a) The dc output voltage the half-wave rectifier should produce
ii ) without a capacitor
V =
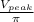
ii) with a capacitor filter
V =
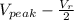 ; where
; where
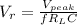
V =
![V_(peak) [ 1 - (1)/(2fR_(l) C) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/4lgnw7n6hsz9yu7e7incsaivaq0r21yyio.png)
b) The dc output voltage the bridge rectifier should produce
i) without a capacitor
V =
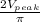
ii ) with a capacitor
V =
![V_(peak) [ 1 - (1)/(4fR_(L)C ) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/d5i7trngzyxmioqvvvu7ndko6ayuadx6sm.png)
2) a) peak reverse voltage in the half-wave rectifier with capacitor in parallel with the load resistor
during -ve half cycle
P/V =
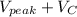
Voltage across capacitor = Vc = Vpeak
Therefor the PIV for a half-wave rectifier with capacitor in parallel
= 2 * Vpeak = 2Vpeak
b) Peak reverse voltage in the bridge rectifier with capacitor in parallel with the load resist
P/ V =