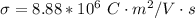Answer:
The value is
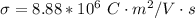
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The mobility of electron in a tiny room is
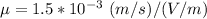
The number of mobile electron per
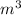 is
is
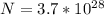
Generally the conductivity is mathematically represented as
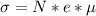
Here
 is the charge on a single electron and that value is
is the charge on a single electron and that value is

So
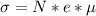
=>
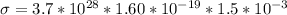
=>