Answer:
The ratio of parent to daughter isotopes is
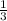 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
We know that Carbon-14 decays in time and transforms into Nitrogen-14, being the latter the "daughter" of the first one. The decay of any isotope is represented by the following ordinary linear differential equation:
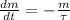 (Eq. 1)
(Eq. 1)
Where:
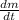 - Rate of change of the isotope mass, measured in grams per year.
- Rate of change of the isotope mass, measured in grams per year.
 - Time constant, measured in years.
- Time constant, measured in years.
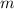 - Current mass of the isotope, measured in grams.
- Current mass of the isotope, measured in grams.
The solution of this differential equation is:
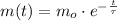 (Eq. 2)
(Eq. 2)
Where:
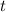 - Time, measured in years.
- Time, measured in years.
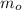 - Initial mass of the isotope, measured in grams.
- Initial mass of the isotope, measured in grams.
Time constant can be found as a function of half life. Please notice that half-life of Carbon-14 is 5760 years. The equation of time constant is:
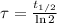 (Eq. 3)
(Eq. 3)
Where
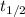 is the half-life of the isotope, measured in years.
is the half-life of the isotope, measured in years.
If we know that
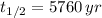 and
and
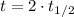 , then we have that:
, then we have that:
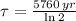
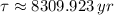
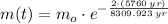
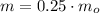
Which means that 75 % of the original mass of Carbon-14 became Nitrogen-14. The parent-to-daughter ratio is:
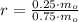
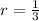
The ratio of parent to daughter isotopes is
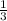 .
.