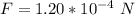Complete Question
A 6.00-µc charge is moving with a speed of 7.50x10^4 m/s parallel to a very long, straight wire. the wire is 5.20 cm from the charge and carries a current of 68.5 A in a direction opposite to that of the moving charge. Calculate the magnitude of the force on the charge.
Answer:
The value is
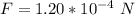
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The magnitude of the charge is
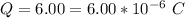
The speed is

The distance of the wire from the charge is
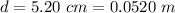
The current flowing through the wire in the opposite direction to the charge is
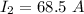
Gnerally the magnitude of force on that charge is mathematically represented as
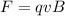
Here B is magnetic field which is mathematically represented as
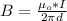
Here
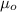 is the permeability of free space with value
is the permeability of free space with value
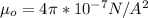
So
![F = qv[(\mu_o * I)/(2\pi d)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/9embwfmig3yo1899ck6aitu2ru1robr8vw.png)
=>
![F = 6.0*10^(-6) * (7.50 *10^(4))[(4\pi * 10^(-7) * 68.5 )/(2* 3.142 * 0.0520 )]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/ngms3ew63i99sbtjdr5qcwv5wv5ndftb9h.png)
=>