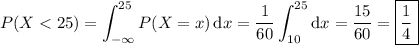If you're talking about a discrete distribution, then
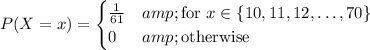
(1/61 because there are 61 numbers in the range of integers from 10 to 70) so that
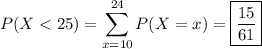
If the distribution is continuous, we would have the same density function, but x can be any real number in the interval [10, 70]. So we have