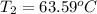Answer:
The temperature is
Step-by-step explanation:
Generally the equation that represents the variation of resistance with respect to temperature is mathematically represented as
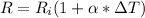
=>
![R = R_i (1 + \alpha * [T_2 - T_1] )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/rgdadzpo95mczmf7hqts06b3o4lte61g3i.png)
Here
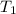 is the original temperature with value
is the original temperature with value
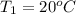
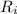 is the initial resistance of the copper
is the initial resistance of the copper
R is the resistance at temperature

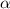 is the temperature coefficient of resistivity with a value
is the temperature coefficient of resistivity with a value
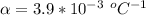
From the question we are told that
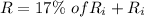
So
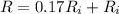
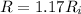
Hence
![1.17 R_i = R_i (1 + 3.9 *10^(-3) * [T_2 - 20] )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/dozvf8avj4g247ig9d6vz3th3ocscigio4.png)
![1.17 = (1 + 3.9 *10^(-3) * [T_2 - 20] )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/tfzzxtks4bqh8qp8ya90r24hm6znfaumyd.png)
=>
![0.17 = 3.9 *10^(-3) * [T_2 - 20] )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/x16ci32u5kiuq55opjzu9jt1c62fzzq3xs.png)
=>
![[T_2 - 20] = 43.5897](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/9fvy45i7ubn99hoqdu1zqo3q5670imdw9i.png)
=>