Answer:
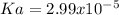
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, as you are not indicating the molarity of the solution and its pH we are going to assume they are 1.4 M and 2.19 respectively as typical problems over this. In such a way, based on the pH we can compute the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution:
![[H^+]=10^(-pH)=10^(-2.19)=6.467x10^(-3)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4ub6dmuizsc4gbn1mu93i3gmuywbc8y306.png)
Next, the dissociation of 4-chlorobutanoic acid is:
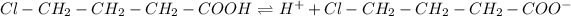
Since it is a weak acid, therefore, its equilibrium expression is:
![Ka=([H^+][Cl-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2-COO^-])/([Cl-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2-COOH])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/en65ynrykl1uacpeqepkqgour1zx5xabcb.png)
Since the concentration of hydrogen ions equal the concentration of 4-chlorobutanoate ions at equilibrium and the concentration the 4-chlorobutanoic acid equals 1.4 M minus the concentration of hydrogen ions, which is related to the reaction extent
 , the acid dissociation constant is:
, the acid dissociation constant is:
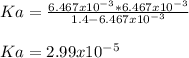
Best regards!