Answer:
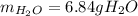
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, for 5.17 g of hexane (molar mass = 86 g/mol) and 16.5 g of oxygen (molar mass =32 g/mol), we have the reaction:
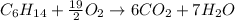
Next, via the 1:7 mole ratio of hexane to carbon dioxide and 19/2:7 mole ratio of oxygen to carbon dioxide, we compute the yielded mass of water (molar mass = 18 g/mol) as its theoretical yield by the two masses of reactants and we infer that the limiting reactant is that yielding the fewest moles of product:
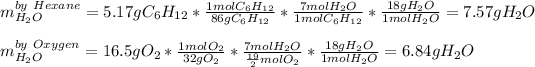
Whereas it is evidenced that oxygen yields the fewest grams of water, therefore, it is the limiting reactant and the theoretical yield of water is:
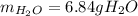
Best regards!