Answer:
d. a) no change in the equilibrium and
b) equilibrium shifts towards products.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, for the reaction:
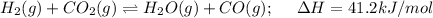
Which is endothermic due to the positive enthalpy of reaction. In such a way, based on the Le Chatelier's principle which states that increasing the temperature of an endothermic chemical reaction shifts the equilibrium towards products as heat is understood as a reactant, we can see, this is the case.
Moreover, since the change in the number of gaseous moles in the chemical reaction (coefficients balancing the reaction) is 0 (1+1-1-1), we can see that increasing the total pressure does not have any effect over equilibrium.
Therefore answer is d. a) no change in the equilibrium and b) equilibrium shifts towards products.
Best regards!