Answer:
If d is zero, both roots are rational and equal.
Explanation:
Quadratic Equations
The standard representation of a quadratic function is:
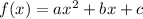
where a,b, and c are constants.
Solving with the quadratic formula:
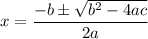
The discriminant is defined as:
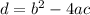
The sign of the discriminant defines the nature of the roots of the quadratic equation as follows:
- If d is positive, both roots are real and different
- If d is negative, both roots are imaginary and conjugate
- If d is zero, both roots are rational and equal.