Answer:
Its rotation will be 3.89x10⁴ rad/s.
Explanation:
We can find the rotation speed by conservation of the angular momentum:
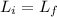
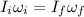 (1)
(1)
The initial angular speed is:
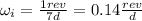
The moment of inertia (I) of a sphere is:
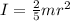 (2)
(2)
Where m is 9 times the sun's mass and r is the sun's radius
By entering equation (2) into (1) we have:
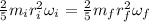
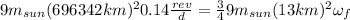
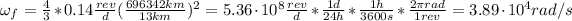
Hence, its rotation will be 3.89x10⁴ rad/s.
I hope it helps you!