Answer:
a
True mean diameter
![[\mu]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/587dfpmzwx9tmeorq5u3op5zr1w70xuq1p.png)
b
The null hypothesis is
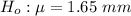
The alternative hypothesis is
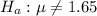
c
Gnerally type I error occurs when the null hypothesis is wrongfully rejected
The consequence of this is that the wrongfully rejecting a batch of needles because the company do not find strong evidence that its true mean diameter is 1.65 mm whereas it is
d
Gnerally type II error occurs when the null hypothesis is wrongfully accepted
The consequence of this is that the wrongfully accepting a batch of needles because the company do find strong evidence that its true mean diameter is 1.65 mm whereas it is not
Explanation:
Generally from the question we are told that
The needle needs to have a diameter of 1.65 mm
Now statistically the parameter of interest in the context of this study is the true mean diameter of the needle and the symbol is

The null hypothesis is
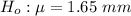
The alternative hypothesis is
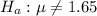
Gnerally type I error occurs when the null hypothesis is wrongfully rejected
The consequence of this is that the wrongfully rejecting a batch of needles because the company do not find strong evidence that its true mean is 1.65 mm whereas it is
Gnerally type II error occurs when the null hypothesis is wrongfully accepted
The consequence of this is that the wrongfully accepting a batch of needles because the company do find strong evidence that its true mean is 1.65 mm whereas it is not