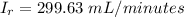Answer:
The values are
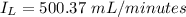
and
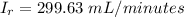
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The pressure at the bifurcation of the femoral artery is

The pressure at the left or right femoral artery is
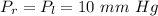
The resistance in the left femoral artery is
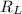
The resistance in the right femoral artery is

The total flow rate is
The diagram illustrating this question is shown on the first uploaded image
Generally this flow of blood through the artery can be compared to the a circuit as shown on the first uploaded image
Generally the rate at which blood flows through the left femoral artery is mathematically represented as
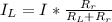
=>
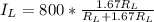
=>
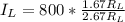
=>
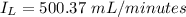
Generally the rate at which blood flows through the right femoral artery is mathematically represented as
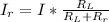
=>
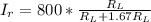
=>
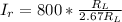
=>