Answer: The molar mass of the unknown gas is 9 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
From Graham's law of effusion rates, the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass.
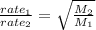
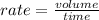
Rate is volume effused per unit time. Since, the volumes are same, the formula could be written as:
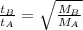
Putting the values in the formula:
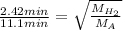
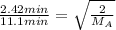
Squaring both sides:
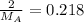
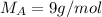
The molar mass of the unknown gas is 9 g/mol