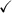Answer: see proof below
Explanation:
Given: cos 330 =
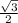
Use the Double-Angle Identity: cos 2A = 2 cos² A - 1
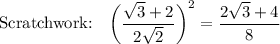
Proof LHS → RHS:
LHS cos 165
Double-Angle: cos (2 · 165) = 2 cos² 165 - 1
⇒ cos 330 = 2 cos² 165 - 1
⇒ 2 cos² 165 = cos 330 + 1
Given:
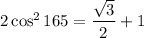
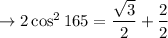
Divide by 2:
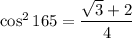
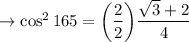
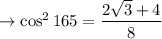
Square root:
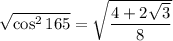
Scratchwork:
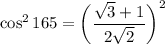
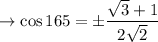
Since cos 165 is in the 2nd Quadrant, the sign is NEGATIVE
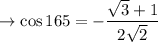
LHS = RHS