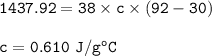The specific heat capacity of the metal : 0.610 J/g° C
Further explanation
The law of conservation of energy can be applied to heat changes, i.e. the heat received/absorbed is the same as the heat released
Q abs = Q received
Heat can be calculated using the formula:
Q = mc∆T
Q = heat, J
m = mass, g
c = specific heat, joules / g ° C
∆T = temperature difference, ° C / K
∆T = T(final temp) - T(initial temp)
mass of metal = 38 g
T initial metal = 92 °C
mass of water = 43 g
T final water = 30 °C
T initial water = 22°C
c water = 4.18 J/g° C
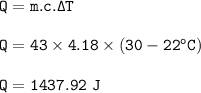
- the specific heat capacity of the metal
Q water = Q metal