Answer:
mole fraction of C6H6 = 0.613 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation for this reaction is :
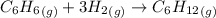
Initial P₁ P₂ 0
Final 0 P₂ -P₁/2 P₁
After completion of the reaction;
P₁ + P₂ = 1.21 atm ----- (1)
P₂ - P₁/2 + P₁ = 0.839 atm
P₂ + P₁/2 = 0.839 atm ----- (2)
Subtracting (2) from (1); we have:
P₁/2 = 0.371
P₁ = 0.742 atm
From(1)
P₁ + P₂ = 1.21 atm
0.742 atm + P₂ = 1.21 atm
P₂ = 1.21 atm - 0.742 atm
P₂ = 0.468 atm
Thus, the partial pressure of C6H6 = 0.742 atm
∴
Partial pressure = Total pressure × mole fraction of C6H6
mole fraction of C6H6 = Partial pressure / Total pressure
mole fraction of C6H6 = 0.742 atm / 1.21 atm
mole fraction of C6H6 = 0.613 atm