Answer:
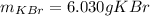
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, since the normal boiling point of X is 117.80 °C, the boiling point elevation constant is 1.48 °C*kg*mol⁻¹, the mass of X is 100 g and the boiling point of the mixture of X and KBr boils at 119.3 °C, we can use the following formula:
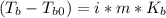
Whereas the Van't Hoff factor of KBr is 2 as it dissociates into potassium cations and bromide ions; it means that we can compute the molality of the solution:
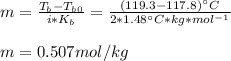
Next, given the mass of solventin kg (0.1 kg from 100 g), we compute the moles KBr:
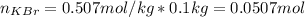
Finally, considering the molar mass of KBr (119 g/mol) we compute the mass that was dissolved:

Best regards.