Answer:
(a) The kinetic energy of the bowling ball just before it hits the matress is 102.974 joules.
(b) The work done by the gravitational force of Earth on bowling ball during the first part of the fall is 102.974 joules.
(c) Work done by gravitational force on bowling ball when mattress is compressed is 10.298 joules.
(d) The work done by the mattress on the bowling ball is 113.272 joules.
Step-by-step explanation:
The statement is incomplete. The complete question is:
In a mattress test, you drop a 7.0 kg bowling ball from a height of 1.5 m above a mattress, which as a result compresses 15 cm as the ball comes to a stop.
(a) What is the kinetic energy of the ball just before it hits the mattress?
(b) How much work does the gravitational force of the earth do on the ball as it falls, for the first part of the fall (from the moment you drop it to just before it hits the mattress)?
(c) How much work does the gravitational force do on the ball while it is compressing the mattress?
(d) How much work does the mattress do on the ball? (You’ll need to use the results of parts (a) and (c))
(a) Based on the Principle of Energy Conservation, we know that ball-earth system is conservative, so that kinetic energy is increased at the expense of gravitational potential energy as ball falls:
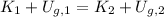 (Eq. 1)
(Eq. 1)
Where:
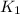 ,
,
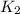 - Kinetic energies at top and bottom, measured in joules.
- Kinetic energies at top and bottom, measured in joules.
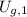 ,
,
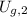 - Gravitational potential energies at top and bottom, measured in joules.
- Gravitational potential energies at top and bottom, measured in joules.
Now we expand the expression by definition of gravitational potential energy:
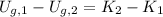
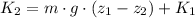 (Eq. 1b)
(Eq. 1b)
Where:
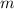 - Mass of the bowling ball, measured in kilograms.
- Mass of the bowling ball, measured in kilograms.
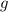 - Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
- Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
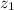 ,
,
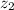 - Initial and final heights of the bowling ball, measured in meters.
- Initial and final heights of the bowling ball, measured in meters.
If we know that
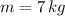 ,
,
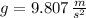 ,
,
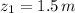 ,
,
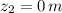 and
and
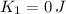 , the kinetic energy of the ball just before it hits the matress:
, the kinetic energy of the ball just before it hits the matress:
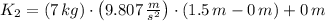
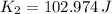
The kinetic energy of the bowling ball just before it hits the matress is 102.974 joules.
(b) The gravitational work done by the gravitational force of Earth (
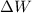 ), measured in joules, is obtained by Work-Energy Theorem and definition of gravitational potential energy:
), measured in joules, is obtained by Work-Energy Theorem and definition of gravitational potential energy:
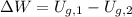
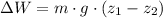 (Eq. 2)
(Eq. 2)
If we know that
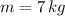 ,
,
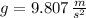 ,
,
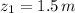 and
and
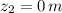 , then the gravitational work done is:
, then the gravitational work done is:
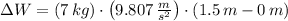
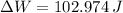
The work done by the gravitational force of Earth on bowling ball during the first part of the fall is 102.974 joules.
(c) The work done by the gravitational force of Earth while the bowling when mattress is compressed is determined by Work-Energy Theorem and definition of gravitational potential energy:
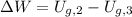
Where
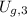 is the gravitational potential energy of the bowling ball when mattress in compressed, measured in joules.
is the gravitational potential energy of the bowling ball when mattress in compressed, measured in joules.
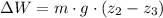
Where
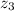 is the height of the ball when mattress is compressed, measured in meters.
is the height of the ball when mattress is compressed, measured in meters.
If we know that
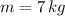 ,
,
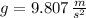 ,
,
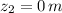 and
and
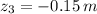 , the work done is:
, the work done is:
![\Delta W = (7\,kg)\cdot \left(9.807\,(m)/(s^(2)) \right)\cdot [0\,m-(-0.15\,m)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/tbv14pkg2ivxfze29qagluh1bn5jcuzfen.png)
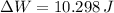
Work done by gravitational force on bowling ball when mattress is compressed is 10.298 joules.
(d) The work done by the mattress on the ball equals the sum of kinetic energy just before mattress compression and the work done by the gravitational force when mattress is compressed:
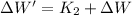
(
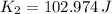 ,
,
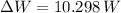 )
)
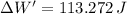
The work done by the mattress on the bowling ball is 113.272 joules.