Answer:
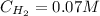
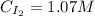
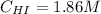
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction is:
H₂(g) + I₂(g) ⇄ 2HI(g)
Initially, we have the following concentrations of H₂ and I₂:
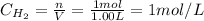
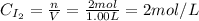
Then, in the equilibrium we have:
H₂(g) + I₂(g) ⇄ 2HI(g)
1-x 2-x 2x
![Kc = ([HI]^(2))/([H_(2)][I_(2)]) = ((2x)^(2))/((1-x)(2-x))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ijygqcbfr2ukctansgnqn3zgjspp3mz3gh.png)
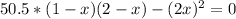
By solving the above equation for x we have:
x₁ = 2.32 and x₂= 0.93
Hence, the concentrations of H₂, I₂ and HI are:



I hope it helps you!