Answer:\
a
The null hypothesis is
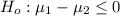
The alternative hypothesis is
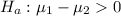
b
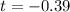
c
The conclusion
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the female outscores the male.
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The sample size for male is
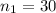
The sample size for female is
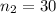
The level of significance is
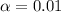
The null hypothesis is
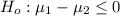
The alternative hypothesis is
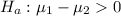
Generally the sample mean for male is
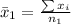
=>
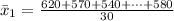
=>
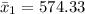
Generally the standard deviation of male is
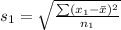
=>
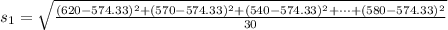
=>
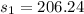
Generally the sample mean for female is
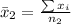
=>
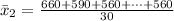
=>
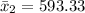
Generally the standard deviation of male is
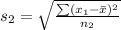
=>

=>
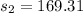
Generally the degree of freedom for unequal variance is mathematically represented as
![df = ([(s_1^2)/(n_1) +(s_2^2)/(n_2) ]^2)/( ([(s_1^2)/(n_1)]^2)/(n_1 -1) +([(s_2^2)/(n_2)]^2)/(n_2 -1) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/1a9pxpm97841tpvrcngo6q9qg50dizyx2n.png)
=>
![df = ([(206.24^2)/(30) +(169.31^2)/(30) ]^2)/( ((206.24^2)/(30))/(30 -1) +((169.31^2)/(30))/(30 -1) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/s3xlknahb9kznexjhkzvnzbuzytgosck6p.png)
=>
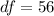
Generally the test statistics is mathematically represented as
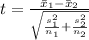
=>
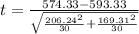
=>
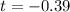
From the t distribution table the value of
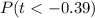 at a degree of freedom of
at a degree of freedom of
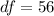 is
is
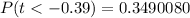
Hence the p-value is
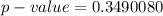
From the values obtained we see that the p-value is >
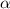
Hence we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
The conclusion is
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the female outscores the male