Answer:
It is statistically significant that mean of difference scores is different from 0
Explanation:
Subject Bar 1 Bar 2 Difference
1 20 40 20
2 18 25 7
3 24 38 14
4 14 27 13
5 5 31 29
6 26 21 -5
7 15 32 17
8 29 38 9
9 15 25 10
10 9 18 9
Mean of difference =
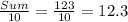
Standard deviation s =
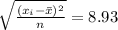
Null Hypothesis : mean of difference scores is 0 :
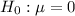
Alternate Hypothesis : mean of difference scores is different from 0 :
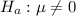
We will use t test for unpaired
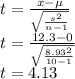
Level of significance (two tailed) =
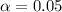
Degree of freedom = n-1 = 10-1 =9
Using calculator
The p-value is .002559.
p value < α
So ,we reject null hypothesis
So, It is statistically significant that mean of difference scores is different from 0