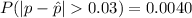Answer:
The probability is
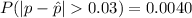
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The population proportion is
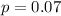
The mean of the sampling distribution is
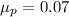
The sample size is n = 600
Generally the standard deviation is mathematically represented as
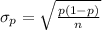
=>
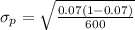
=>
Generally the probability that the proportion of airborne viruses in a sample of 600 viruses would differ from the population proportion by greater than 3% is mathematically represented as
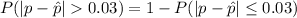
=>
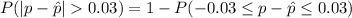
Now add p to both side of the inequality
=>
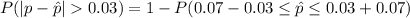
=>
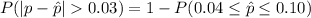
Now converting the probabilities to their respective standardized score
=>
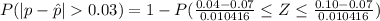
=>

=>
![P(|p-\^(p)| > 0.03) = 1 - [P(Z \le 2.88) - P(Z \le -2.88)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/4qg22ty7om99xm5tjbs79iun7omf0k8q24.png)
From the z-table
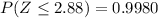
and
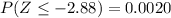
So
![P(|p-\^(p)| > 0.03) = 1 - [0.9980 - 0.0020]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/urhviwpa6ue1dqgnmjgreatm112yp2jp5h.png)
=>