Answer:
i. When the temperature is above
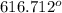 F, it changes to gas.
F, it changes to gas.
ii. When the temperature is below
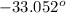 F, it changes to solid.
F, it changes to solid.
Explanation:
Matter generally exists in either a solid, liquid or gaseous form. With each phase having a certain range of temperature.
Temperature scale of a given substance can be either in Celsius, Fahrenheit or Kelvin. And conversion from one scale to another can be achieved. Example, Celsius scale can be converted to Fahrenheit by:
F =
 θ + 32
θ + 32
where: F is the equivalent temperature in Fahrenheit, θ is the value of temperature in degree Celsius.
Given that: melting point of the substance =
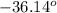 C
C
⇒ F =
 x
x
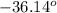 + 32
+ 32
=
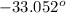 F
F
The boiling point =
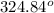 C
C
F =
 x
x
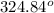 + 32
+ 32
=
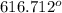 F
F
The melting point of the substance is
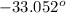 F, and boiling point is
F, and boiling point is
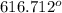 F.
F.
Therefore, the range of temperatures for which the substance is not in a liquid state are:
i. When the temperature is above
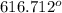 F, it changes to gas.
F, it changes to gas.
ii. When the temperature is below
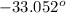 F, it changes to solid.
F, it changes to solid.