Given:
In ΔGHI, GI is extended through point I to point J.
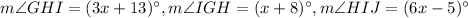
To find:
The measure of angle GHI.
Explanation:
According to exterior angle theorem, the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of measure of two opposite angles.
Using exterior angle theorem, we get
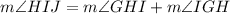
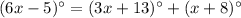
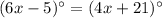
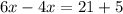
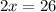
Divide both sides by 2.
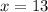
Now,
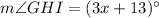
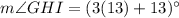
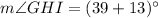
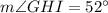
Therefore, the measure of angle GHI is 52 degrees.