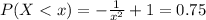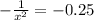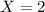Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
a
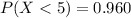
b
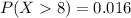
c
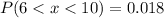
d
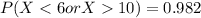
e
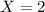
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The probability density function is
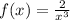 for x > 1
for x > 1
Considering question a
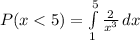
=>
![P(X < 5) = [-(1)/(x^2) ]| \left \ 5} \atop {1}} \right.](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/r5u3ythdvbn9t95dw6dzshlkp2gu8lpbg5.png)
=>
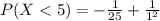
=>
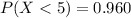
Considering question b
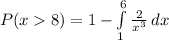
=>
![P(X > 8) =1- [-(1)/(x^2) ]| \left \ 8} \atop {1}} \right.](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/1p3f682lnnwe4bp1q7me1dsh1w3botllsq.png)
=>
![P(X > 8) = 1 - [- (1)/(64) + (1)/(1^2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/1j58olhzegaszz2nsvr6g0e3v3k9dy9t3v.png)
=>
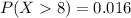
Considering question c
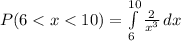
=>
![P(6 < x < 10) = [-(1)/(x^2) ]| \left \ 10} \atop {6}} \right.](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/pe440mdqbyx4n5dds022y56hgz4kit2gm3.png)
=>
![P(6 < x < 10) = [- (1)/(100) + (1)/(36)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/zfzakm4yqu9fytr0fo2rhk3q0d1zbaqlpq.png)
=>
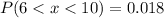
Considering question d
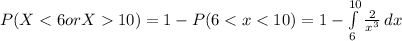
=>
![P(X < 6 or X > 10 ) =1- [-(1)/(x^2) ]| \left \ 10} \atop {6}} \right.](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ea810dem2ellp21ljcqzmxr6m54syj7wk7.png)
=>
![P(X < 6 or X > 10 ) =1- [- (1)/(100) + (1)/(36)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/g7ahaijxy2ogu1bryzdj9vycg2u1r2f8we.png) [/tex]
[/tex]
=>
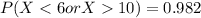
Considering question e
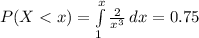
![P(X < x ) = [- (1)/(x^2) ]| \left \ x } \atop {1}} \right. = 0.75](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/yks9bedvi0004m9uaw003ug9ebsu4yc1xa.png)
![P(X < x ) = - (1)/(x^2) - [- (1)/(1^2) ]= 0.75](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/iev7m7hbj9vleuw5s39qg2vzvwsm6mxtob.png)