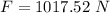Answer:
a
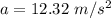
b
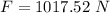
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The length of the Chinook salmon is
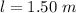
The mass of the Chinook salmon is
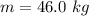
The upward velocity in water is
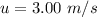
The upward velocity in air is
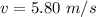
Generally from kinematic equations
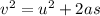
=>
![5.80^2 = 3.00^2 + 2 * a * [ [(2)/(3) * l ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/511ly1cm4s4cpzy4w3gsmo01b06v675rgp.png)
=>
![5.80^2 = 3.00^2 + 2 * a * [ [(2)/(3) * 1.5 ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/fvzq1z7pvmlhf5r6hunq4d8dp2rjlp7gtj.png)
=>
![5.80^2 = 3.00^2 + 2 * a * [1 ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/1iqjfi4vxx5eur6jwet4zigyfdz69mosrh.png)
=>
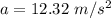
Generally magnitude of the force F during this interval in N is mathematically represented as
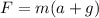
=>
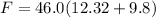
=>