Answer:
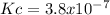
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, for the chemical reaction:
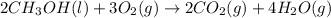
We write the equilibrium expression including the gaseous or aqueous species only, that is why the methanol is not included due to heterogeneous equilibrium:
![Kc=([CO_2]^2[H_2O]^4)/([O_2]^3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/tz02n3aiyz9apyog38p4wwiz7o0me2y52o.png)
Whereas each gaseous species is powered to its stoichiometric coefficient (number before the species). In such a way, considering the equilibrium masses of carbon dioxide (44 g/mol), water (18 g/mol) and oxygen (32 g/mol) to be 1.56 g, 2.28 g and 3.33 g respectively, we compute the moles as we need molar concentrations in the equilibrium constant calculation:
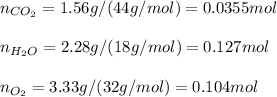
Thus, into the 9.3.L vessel, the equilibrium concentrations are:
![[CO_2]=(0.0355mol)/(9.3L)=0.00382M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ty5f69l0kcf2z4nh5ul1ootm71pfov7c0e.png)
![[H_2O]=(0.127mol)/(9.3L)=0.0137M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/umf85xonc6kd4hf00vfszfqwa5p8hvhc3x.png)
![[O_2]=(0.104mol)/(9.3L)=0.0112M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/n075kygbfif9ojnkss2ok31p5i1wauqys9.png)
Therefore, the equilibrium constant shown with two significant figures is:
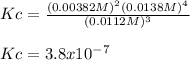
Best regards.