Answer:
$221.44
Explanation:
As the bank charges a monthly interest, we cannot calculate a simple or compound interest over the 8 month period. As the balance will decrease each month as Kylie makes payments, the interest applied each month will also decrease. Therefore, we have to use:
Monthly Payment Formula
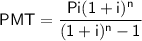
where:
- PMT = monthly payment
- P = loan amount
- i = interest rate per month (in decimal form)
- n = term of the loan (in months)
Given:
- P = $1,700
- i = 0.925% = 0.00925
- n = 8 months
Substituting the given values into the formula and solving:
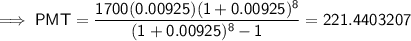
Therefore, the monthly payment to the nearest dollar will be $221.44