Answer:
(a) 1.6 N/C, due east.
(b) 4 N/C, due east.
Step-by-step explanation:
The force vector,
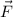 on the charge, q, in the electric field vector,
on the charge, q, in the electric field vector,
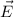 , is
, is
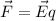
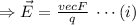
Let the unit vector towards east is
 , so the unit vector towards west is -
, so the unit vector towards west is -
(a) Given that:
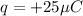 ,
,
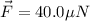 , due east
, due east
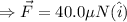
From equation (i)
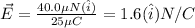
So, the magnitude of electric field is 1.6 N/C and the direction is towards east.
(b) Given that:
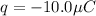 ,
,
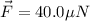 , due west
, due west
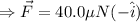
From equation (i)
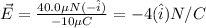
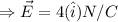
So, the magnitude of electric field is 4 N/C and the direction is towards the east.