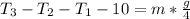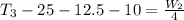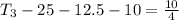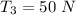Answer:
The force on each wire is
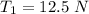
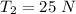
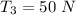
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The acceleration at which the elevator will stop is
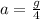
The weight of each section of the wire is
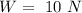
Generally
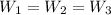 here
here
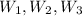 are weight at each section
are weight at each section
Generally considering the first section, the force acting along the y-axis is mathematically represented as
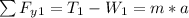
Here
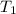 represents the tension on the wire at the first section while
represents the tension on the wire at the first section while
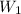 represents the weight of the lamp at the first section
represents the weight of the lamp at the first section
So
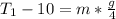
=>
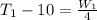
=>
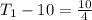
=>
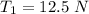
Generally considering the second section, the force acting along the y-axis is mathematically represented as
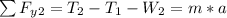
=>
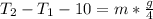
=>
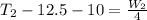
=>
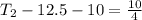
=>
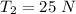
Generally considering the third section, the force acting along the y-axis is mathematically represented as