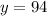Answer:
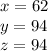
Explanation:
Let's start by identifying relevant angle theorems for two parallel lines cut by a transversal.
Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
Two angles that are on different sides of the transversal and inside of the two parallel lines are congruent (=).
Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
Two angles that are on different sides of the transversal and outside of the two parallel lines are congruent (=).
Same-side Interior Angles Theorem
Two angles that are on the same side of the transversal and inside of the two parallel lines are supplementary (= 180).
Same-side Exterior Angles Theorem
Two angles that are on the same side of the transversal and outside of the two parallel lines are supplementary (=180).
Corresponding Angles Theorem
Two angles on a figure that correspond are congruent (=).
_
Now, let's look at the figure and apply these theorems.
 and
and
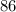 are same-side exterior angles, meaning they're supplementary:
are same-side exterior angles, meaning they're supplementary:
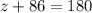
Subtract
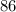 from both sides of the equation:
from both sides of the equation:
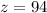
Now that we know our
 value, let's recognize that
value, let's recognize that
 (
(
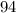 )corresponds to
)corresponds to
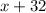 , meaning they're congruent:
, meaning they're congruent:
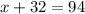
Subtract
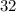 from both sides of the equation:
from both sides of the equation:
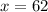
Let's find the value of the angle:
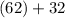
Add:
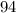
Since the corresponding angles are of the same value, they're congruent, proving our
 &
&
 values correct.
values correct.
_
Since
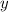 and the angle represented by the expression
and the angle represented by the expression
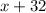 (
(
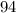 °) are alternate-interior angles, they are congruent:
°) are alternate-interior angles, they are congruent: