Answer:
When the null hypothesis is rejected
The conclusion is that there is enough evidence to support the claim of the researcher
When a type I error occurs
The consequences is that the conclusion that there is enough evidence to support the claim of the researcher is actually incorrect
When a type II error occurs
The consequences is that the conclusion that there is enough evidence to support the claim of the researcher is actually correct
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The cost of electricity per month is
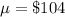
The null hypothesis is
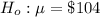
The alternative hypothesis is
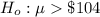
Generally if the null hypothesis is rejected then the conclusion would be that there is enough evidence to support the claim of the researcher
Generally a Type I error is a an error that occurs when the null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected
So in the case of this question the consequence of making this type of error is that the conclusion that there is enough evidence to support the claim of the researcher is actually incorrect
Generally a Type II error is an error that occurs when the null hypothesis is incorrectly not rejected
So in the case of this question the consequence of making this type of
error is that the conclusion that there is enough evidence to support the claim of the researcher is actually correct