Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
The 95% confidence interval is
![[670.03 , 673.97 ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ikyr1g9g85ezcjmoxt3i6djyqcz8d48fk7.png)
The test statistics is
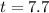
The p-value is
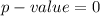
The p-value suggests that the null hypothesis is rejected with a high degree of confidence. Hence there is statistically significant evidence that the districts with smaller classes have higher average test score
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The sample size is n = 408
The sample mean is
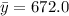
The standard deviation is
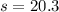
Given that the confidence level is 95% then the level of significance is
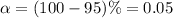
From the normal distribution table the critical value of
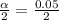 is
is
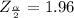
Generally the margin of error is mathematically represented as
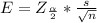
=>
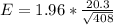
=>
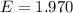
Generally the 95% confidence interval is mathematically represented as
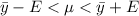
=>
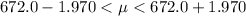
=>
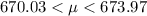
=>
![[670.03 , 673.97 ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ikyr1g9g85ezcjmoxt3i6djyqcz8d48fk7.png)
From the question we are told that
Class size small large
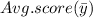
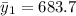
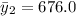
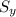
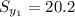
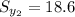
sample size
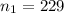

The null hypothesis is
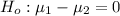
The alternative hypothesis is
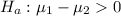
Generally the standard error for the difference in mean is mathematically represented as
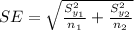
=>
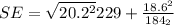
=>
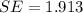
Generally the test statistics is mathematically represented as
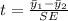
=>
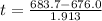
=>
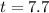
Generally the p-value is mathematically represented as
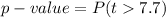
From the z-table
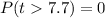
So
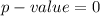
From the values we obtained and calculated we can see that
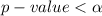
This mean that
The p-value suggests that the null hypothesis is rejected with a high degree of confidence. Hence there is statistically significant evidence that the districts with smaller classes have higher average test score