Given parameters:
Initial volume = 120ml
Initial temperature = 35°C
Initial pressure = 1.2bar
Final volume = 180ml
Final temperature = 35°C
Unknown:
Final pressure = ?
To solve this problem, we apply the combined gas law. The expression is given below;
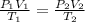
Where P₁ is the initial pressure
P₂ is the final pressure
V₁ is the initial volume
V₂ is the final volume
T₁ is the initial temperature
T₂ is the final temperature
We need to convert the parameters to standard units
take the volume to dm³;
1000ml = 1dm³
120ml =
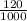 dm³ = 0.12dm³ = initial volume
dm³ = 0.12dm³ = initial volume
Final volume;
1000ml = 1dm³
180ml =
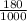 dm³ = 0.18dm³
dm³ = 0.18dm³
Now, the temperature;
K = 273 + °C
Initial temperature = 273 + 35 = 308k
Final temperature = 308k
We then input the parameters into the equation;
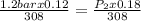
Solving for P₂;
P₂ = 0.8bar
The new pressure or final pressure in the vessel is 0.8bar