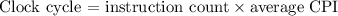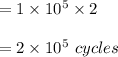Answer:
Follows are the solution to this question:
Step-by-step explanation:
The architecture of two separate iterations with the same the instruction set can be defined in the attached file please find it.
Calculating the value of total instruction count:
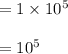
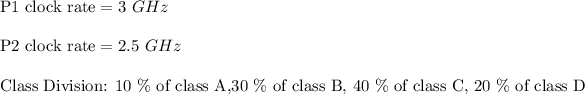
In point a:
Calculating P1 device mean CPI:
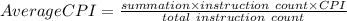
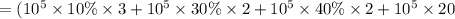
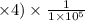
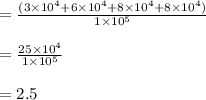
Estimating P2 device Average CPI:
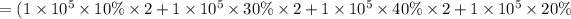
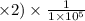
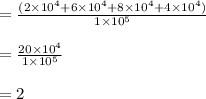
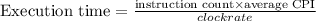
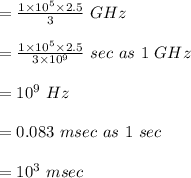
Calculating processor execution time P2:

Since P2 is less than P1 for processor execution time, P2 is therefore faster than P1.
In point b:
Global processor P1 CPI = 2.5
Global processor P2 CPI = 2
In point c:
Finding Processor P1 clock cycles:
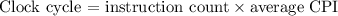
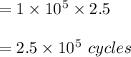
Finding Processor P2 clock cycles: