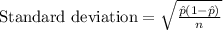Answer:
Following are the answer to the given points.
Explanation:
In point a:
The confidence interval for p is 95%
using formula:
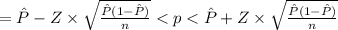
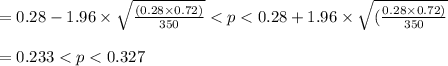
In point b:
Because 0.22 is not within the trust interval, they have enough proof of H0 at level 0.05.
In point c:
For the percentage for samples,
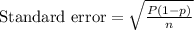 from ratio p
from ratio p
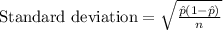 from sample ratio
from sample ratio
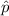
In point d:
Standard deviation is used to measure the interval of confidence